
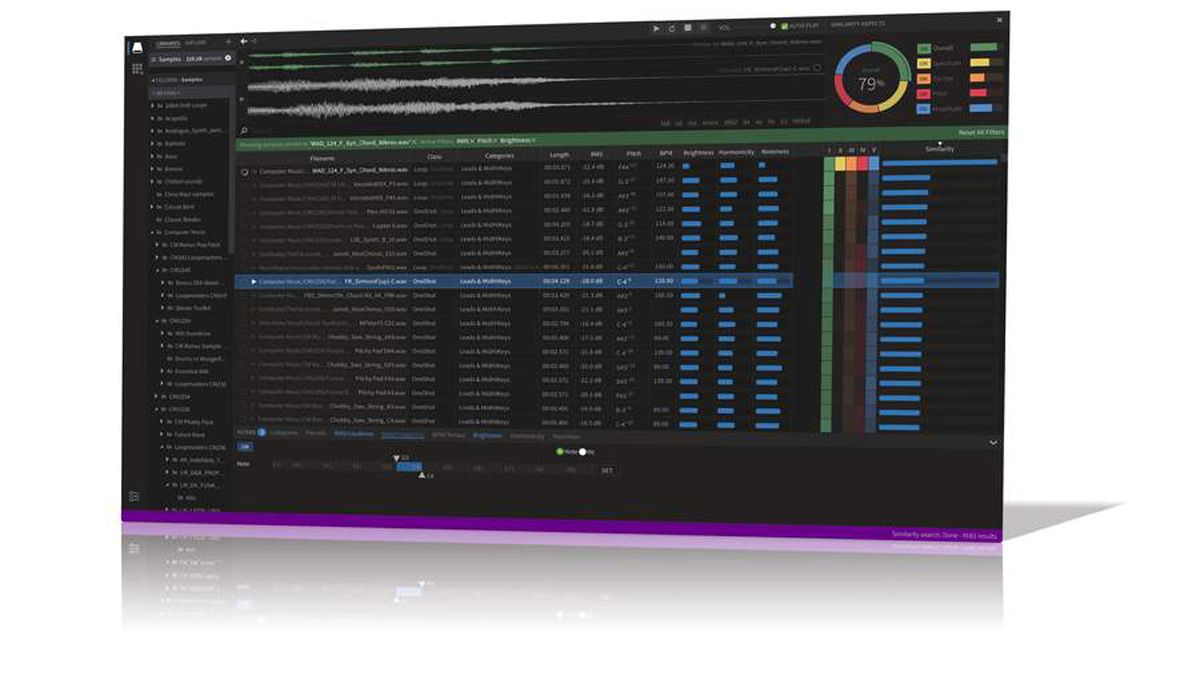
When Sun and Moon are exactly in line, because the Moon is smaller, the Sun appears as a bright ring (annulus) surrounding the moon.Īntimatter is matter composed of anti-particles: antiprotons, antineutrons, and positrons. The property of being anisotropic and having a different value when measured in different directions.Īnnular eclipse, a solar eclipse in which the moon covers all but the bright ring around the circumference of the sun. It is a measure of how large an object actually appears to be.Īnisotropy is the state of being directionally dependent. In astronomy the angular distance of a heavenly body above the horizon.Īnaglyph is a composite picture printed in two colors to produce a 3D image viewed through eye glasses having lenses of the same colors.Īndromeda galaxy is a spiral galaxy that is nearly two and a half million light years away in the constellation Andromeda.Īngular size is the angle between two lines of sight to its two opposite sides. It is the ratio of total-reflected light.Īltazimuth mount is a two-axis mount used to support and rotate an instrument in two common perpendicular axes, vertical (altitude) and horizontal (azimuth).Īltitude is the height of anything above given a planetary reference plane. It is used to remove atmospheric distortion through the use of astronomical telescopes and laser communication.Īiry disk – Named after George Airy, it is the central spot in a diffraction pattern of a stars image in focus in a telescope.Īlbedo is the ratio that light is reflected by a planet or satellite to that received by it. As the name suggests, it works by “actively” adjusting the telescope mirrors.Īdaptive optics – technology used to improve performance of optical systems through the reduction of rapidly changing optical distortion. The construction enables telescopes to move 8 meter primary mirrors. It is a class of galaxies that emit a large amount of energy from their center more than ordinary galaxies.Īctive optics – Technology developed in the 80’s for reflecting telescopes. Achromatic lenses are used to take chromatic aberrations away from images.Īctive galactic nucleiis a region in the center of a galaxy that has a higher than normal brightness.
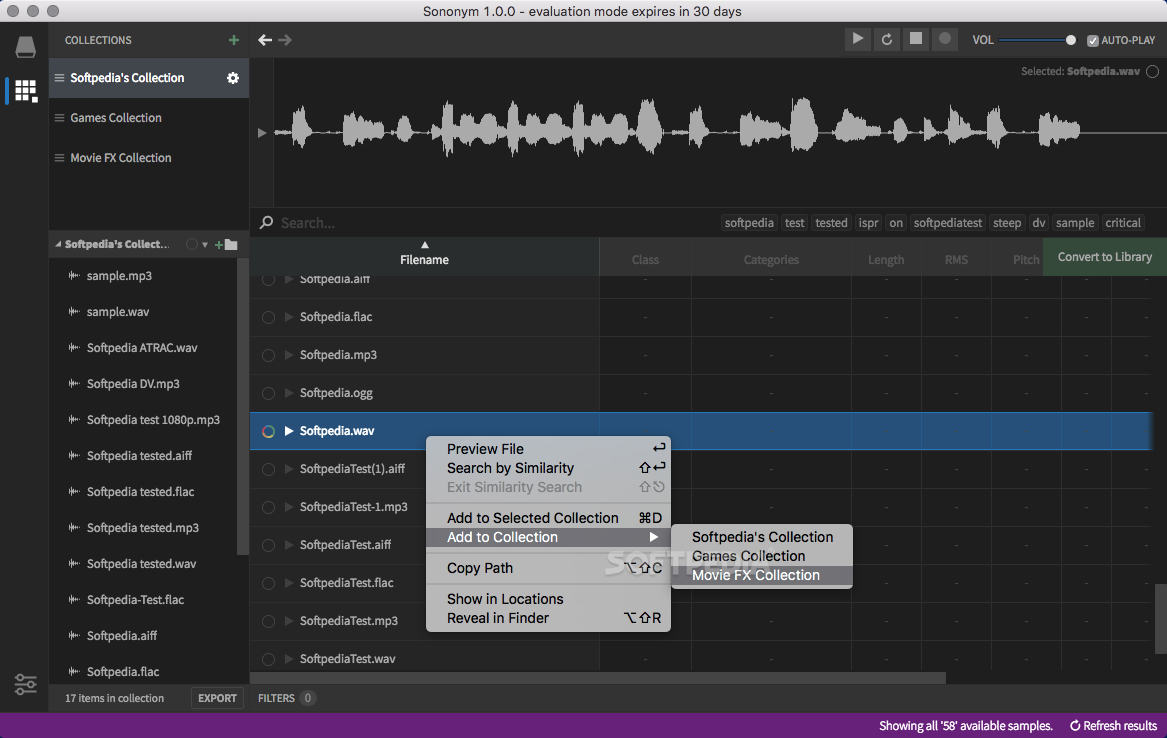
These bring two wavelengths into focus (normally red & blue) on the same plane. There are two places astronomers find accretion disks, binary star systems and galactic nuclei.Īchromatic lens is a combination of lenses made of different glass.
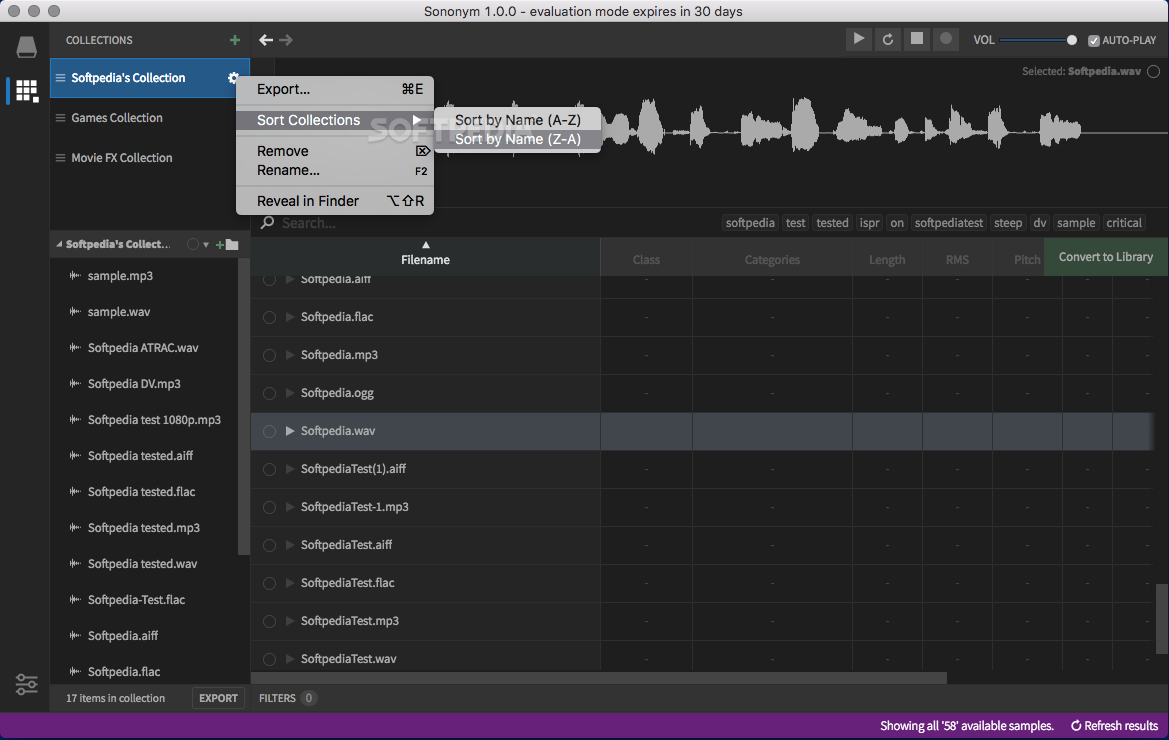
It is the theoretical temperature entropy reaches its minimum value.Ībsorption lines are a dark feature in the spectrum of a star formed by cooler gases in a star’s outer layer.Īccretion disks arise when material, usually gases, are transferred from one celestial object to another. The following are terms from A-Z related to space & astronomy:Ībsolute magnitude – also known as absolute visual magnitude, relates to measuring a heavenly object’s brightness when viewed from 10 parsec or 32+ light years.Ībsolute zero – The international community agreed to define absolute zero as equivalent to −273.15☌ on the Celsius scale or−459.67☏ on the Fahrenheit scale. It may be a synonym of "seminorm".If you ever wonder the meaning of an astronomical word, search no further and browse below to find the definition of the space term. The term pseudonorm has been used for several related meanings.
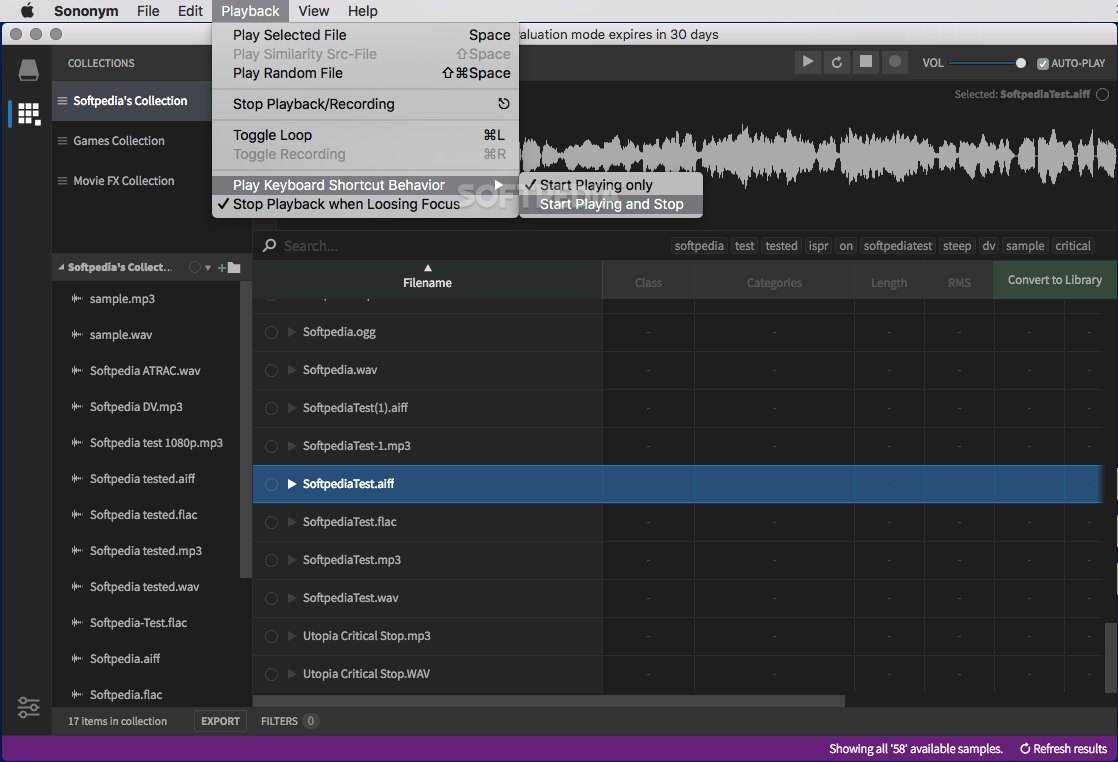
In a similar manner, a vector space with a seminorm is called a seminormed vector space. A vector space with a specified norm is called a normed vector space. This norm can be defined as the square root of the inner product of a vector with itself.Ī seminorm satisfies the first two properties of a norm, but may be zero for vectors other than the origin. In particular, the Euclidean distance in a Euclidean space is defined by a norm on the associated Euclidean vector space, called the Euclidean norm, the 2-norm, or, sometimes, the magnitude of the vector. In mathematics, a norm is a function from a real or complex vector space to the non-negative real numbers that behaves in certain ways like the distance from the origin: it commutes with scaling, obeys a form of the triangle inequality, and is zero only at the origin. For norms in descriptive set theory, see prewellordering. This article is about norms of normed vector spaces.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
